Anxiety disorder is a mental health condition characterized by excessive, persistent worry or fear that can interfere with daily activities. While it’s normal to feel anxious in certain situations, people with anxiety disorders experience these feelings more frequently and intensely. There are several types of anxiety disorders, including:
1. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
- Characterized by chronic, excessive worry about a variety of everyday issues like health, work, or social interactions.
- People often anticipate disaster and may struggle to control their worry, even if there is no immediate threat or reason for concern.
- Symptoms include restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, irritability, muscle tension, and sleep disturbances.
2. Panic Disorder
- Involves recurrent, unexpected panic attacks—sudden episodes of intense fear that trigger severe physical reactions.
- Panic attacks can feel like heart attacks, with symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, dizziness, or feelings of impending doom.
- People with panic disorder often live in fear of having another attack, which can lead to avoiding situations where attacks might occur.
3. Social Anxiety Disorder (Social Phobia)
- Marked by a fear of being judged or embarrassed in social situations.
- People with this disorder may avoid public speaking, attending parties, or other social events because of the fear of scrutiny.
- Physical symptoms might include blushing, sweating, trembling, nausea, or difficulty speaking.
4. Specific Phobias
- Involves an intense, irrational fear of a specific object or situation, such as heights, flying, or certain animals.
- The fear leads to avoidance behavior and can disrupt normal life activities.
5. Agoraphobia
- Fear of being in situations where escape might be difficult or help wouldn’t be available if something goes wrong.
- This can result in avoiding public spaces, crowds, or even leaving home altogether.
6. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- Though not always classified as an anxiety disorder, it involves persistent, unwanted thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions).
- People with OCD perform rituals to ease their anxiety, like excessive cleaning or checking, but these actions only provide temporary relief.
7. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- PTSD can develop after exposure to a traumatic event, such as war, assault, or disaster.
- Symptoms include flashbacks, nightmares, severe anxiety, and uncontrollable thoughts about the event.
Symptoms of Anxiety Disorders:
- Persistent worry or fear.
- Restlessness or feeling on edge.
- Difficulty concentrating.
- Muscle tension or aches.
- Rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling.
- Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia.
- Fatigue and irritability.
Treatment
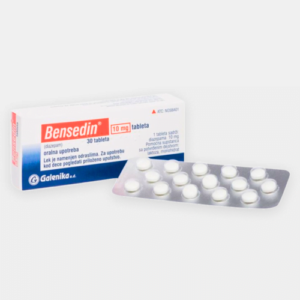
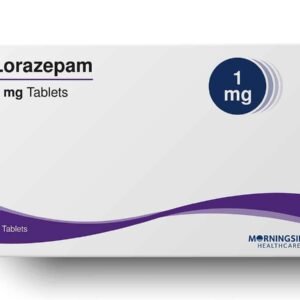
Anxiety disorders are treatable, often with a combination of therapy, medication, or both. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is commonly used to help people manage their anxiety by changing thought patterns. Medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or benzodiazepines like diazepam can be prescribed to help reduce symptoms.
ANTI-ANXIETY
Anxiety disorder
ANTI-ANXIETY
Anxiety disorder